|
|
|
|
Fatigue Fracture |
|
4. PWAs: Fatigue fracture - no mechanical support
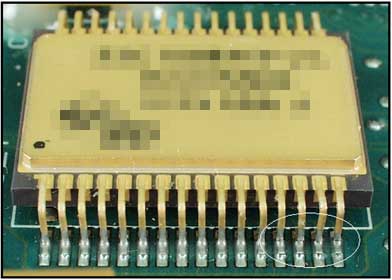
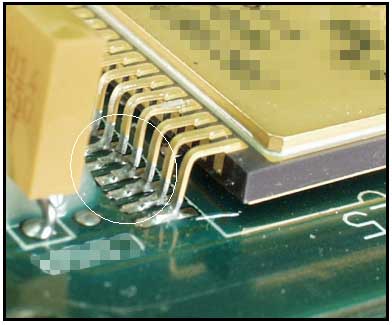
The circles highlight broken leads that fractured during vibration testing in a manner similar to that discussed elsewhere in this gallery (see fractured leads-qfpga.doc). These are also due to fatigue fracture, however, unlike the other example that had inadequate mechanical support, these had none. A part with leads on only 2 sides is more susceptible to damage than a quad-pack device because: a) there are less leads to share the load(s); and b) there is nothing to dampen loads in the axis perpendicular to the leads.
Reference :
NASA-STD-8739.1, 4.4 Principles of Reliable Staking and Conformal Coating. 3. Design Considerations for Staking
The staking material selected shall provide adequate mechanical support to allow the item to survive vibration levels imposed during end-item use. Rigid staking material with a low thermal expansion coefficient is generally desirable. For special cases where parts sensitive to thermal/mechanical stress are used, application of resilient materials may be required.
|
|
|
|
|









